What is an automatic transfer switch?
Is your business vulnerable to a sudden power outage? Losing electricity can stop production, corrupt data, and damage your reputation, costing you more than just a few dark hours.
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is a device that automatically transfers a power load from the main utility source to a backup source, like a generator, during an outage. It then switches back once the main power is restored, ensuring continuous, reliable electricity without manual intervention.

I once got a frantic call from a client who ran a small data center. A brief power outage corrupted a huge amount of data because someone couldn't get to the facility and switch to the backup generator fast enough. That single incident cost them more than ten ATS units would have. This taught me a valuable lesson that I now share with all my clients at YOGU Electric: an ATS isn't just a switch; it's essential insurance for your operations. Let's explore what it really does and why it's so critical for any serious backup power system.
What is the use of an automatic transfer switch?
Are manual generator startups too slow and risky during an outage? This downtime can damage your expensive equipment and lead to lost revenue while you scramble to restore power.
The main use of an ATS is to ensure seamless business continuity1. It provides a reliable and fast switch to backup power for critical loads2 in places like hospitals, data centers3, and manufacturing plants, preventing operational downtime and data loss.
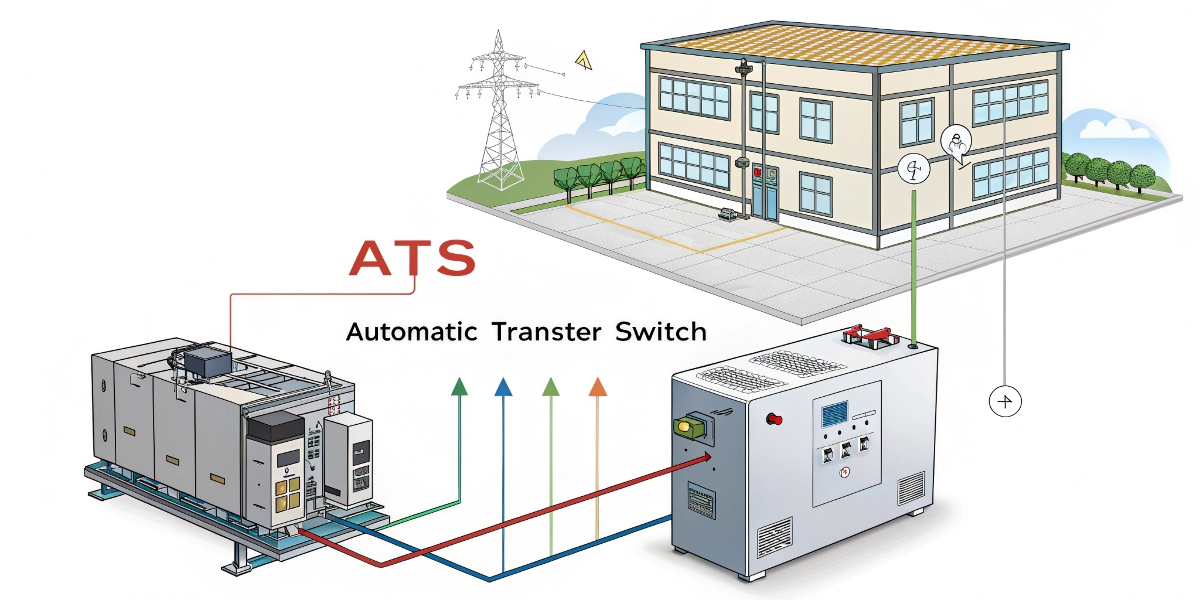
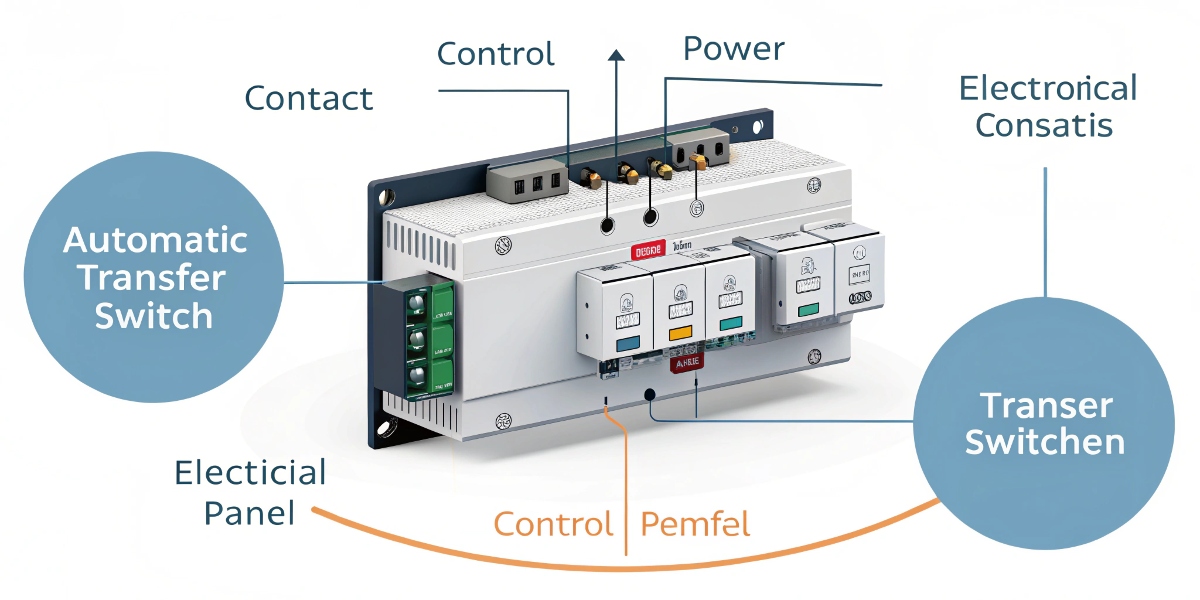
The core purpose of an ATS is to make your backup power system truly automatic and reliable. For a purchasing manager like Mohammed, the value is in protecting the company's assets and ensuring operations continue smoothly. Think about critical applications. In a hospital, a power loss of even a few seconds can be life-threatening. In a data center, it means lost information. In a factory, it means a halt in production. The ATS stands as the guard that instantly responds to a power failure4. It isolates the facility from the utility line to prevent dangerous backfeeding, which can endanger utility workers, and then safely connects the generator. This fully automated process ensures that your most sensitive and important equipment is protected from the chaos of a power outage. It's the critical link that makes your generator a complete, hands-off solution.
Key Applications and Benefits
- Life Safety: Keeps critical systems like emergency lighting, fire pumps, and medical equipment running in hospitals and public buildings.
- Business Continuity: Prevents downtime in data centers, banks, and manufacturing lines where continuous operation is essential.
- Equipment Protection: Protects sensitive electronics from voltage sags and surges5 that occur during power failures and restorations.
What is the disadvantage of an automatic transfer switch?
Do you want automated power but are worried about the drawbacks? Making a bad investment can sometimes create more problems than it solves, so it's important to know the full picture.
The primary disadvantage of an ATS is the initial cost, as it is a significant investment compared to a manual switch. It also requires professional installation and periodic maintenance to ensure its reliability, adding to the total cost of ownership over its lifespan.

It's true that an ATS costs more upfront than a simple manual switch. The installation is also more complex and must be done by a qualified professional. You also need to plan for regular testing and maintenance. If an ATS is not maintained, it can become a single point of failure itself. However, it's a matter of weighing the costs against the risks. A manual switch is cheaper, but it relies on a person being available, being trained, and acting quickly in a crisis. When I talk with purchasing managers, I ask them to consider not just the price of the switch, but the price of failure. What does one hour of downtime cost your business? Usually, that number is much higher than the cost of an ATS. Modern smart ATS units also help reduce the maintenance burden by sending alerts and running self-diagnostics, making them more reliable than ever.
Manual vs. Automatic Transfer Switch
| Feature | Manual Transfer Switch | Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low | High |
| Transfer Speed | Slow (minutes) | Fast (seconds) |
| Reliability | Depends on human operator | High, system-driven |
| Safety | Risk of human error | High, automated safety protocols |
| Convenience | Low, requires on-site action | High, fully automatic 24/7 |
How does an ATS work?
Does the process inside an automatic transfer switch seem like a complex mystery? Buying a piece of equipment is always easier when you understand exactly what it does and how it works.
An ATS continuously monitors the incoming utility power. When it detects a failure or a significant voltage drop, it signals the backup generator to start. Once the generator is ready, the ATS safely disconnects the load from the utility and connects it to the generator.
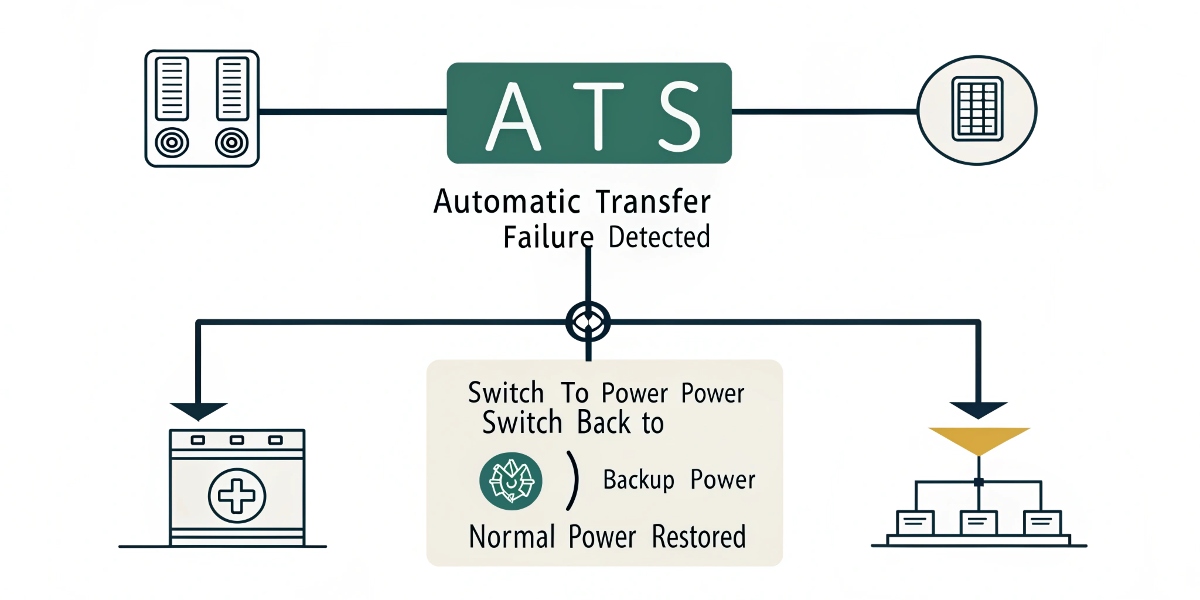
The "magic" inside an ATS is actually a very logical, step-by-step sequence controlled by a small computer, or controller. This controller is the brains of the operation. It ensures a safe and orderly transfer of power, protecting both your equipment and your power sources. My team and I always emphasize that a good ATS does its job so smoothly, you might not even realize the power went out until you see a notification. The process works just as smoothly in reverse when the main power comes back on, ensuring a stable return to normal operations without any disruption.
The Switching Sequence
- Monitor: The ATS controller constantly watches the quality of the utility power.
- Detect: It senses when the voltage drops below a preset level for a specific time. This means the power has failed.
- Signal: It sends a start signal to the backup generator.
- Isolate & Transfer: Once the generator is running at the correct speed and voltage, the ATS disconnects from the utility line. It then connects the building's circuits to the generator.
- Re-transfer: When utility power returns and is stable, the ATS switches back to the utility, signals the generator to cool down, and then shuts it off.
Do I need an automatic transfer switch on my generator?
You invested in a backup generator, but is that actually enough? A generator you have to start by hand in the middle of an emergency might not provide the protection you really need.
Yes, you need an ATS if your goal is immediate, automatic backup power without human intervention. For critical systems where even a few minutes of downtime is unacceptable, or for ultimate safety and convenience, an ATS is essential. A manual switch is only suitable for non-essential loads.

Simply having a generator is only half of a backup power solution. The ATS is the other half that brings it to life when you need it most. For a purchasing manager like Mohammed, deciding whether an ATS is necessary comes down to analyzing risk and operational needs. If you are protecting a home or a small shop where you can afford a few minutes of downtime, a manual switch might work. But if you are managing power for a commercial building, an industrial project, or any operation where downtime equals lost money or high risk, an ATS is not a luxury—it's a requirement. It's also a scalable solution. As your business grows and power needs increase, a properly sized ATS system can grow with you.
Questions to Ask Before You Decide
- What is the total cost of one hour of downtime for our business?
- Do we have servers, HVAC systems, or other equipment that could be damaged by a sudden outage?
- Is someone always on-site 24/7 who is trained to safely operate a manual switch?
- Do our client contracts or industry regulations require a specific level of power uptime?
Conclusion
An ATS is vital for automatic power switching. It ensures business continuity1, protects valuable equipment, and enhances safety. It's a key investment for any truly reliable backup power system.
-
Explore how maintaining business continuity can save your organization from significant losses during power failures. ↩ ↩
-
Identifying critical loads helps prioritize power supply during outages, ensuring essential operations remain functional. ↩
-
Data centers require constant power; learn how ATS protects them from downtime. ↩
-
Learn how an ATS responds to power failures to minimize downtime and protect operations. ↩
-
Learn how voltage fluctuations can damage equipment and how ATS can mitigate these risks. ↩

